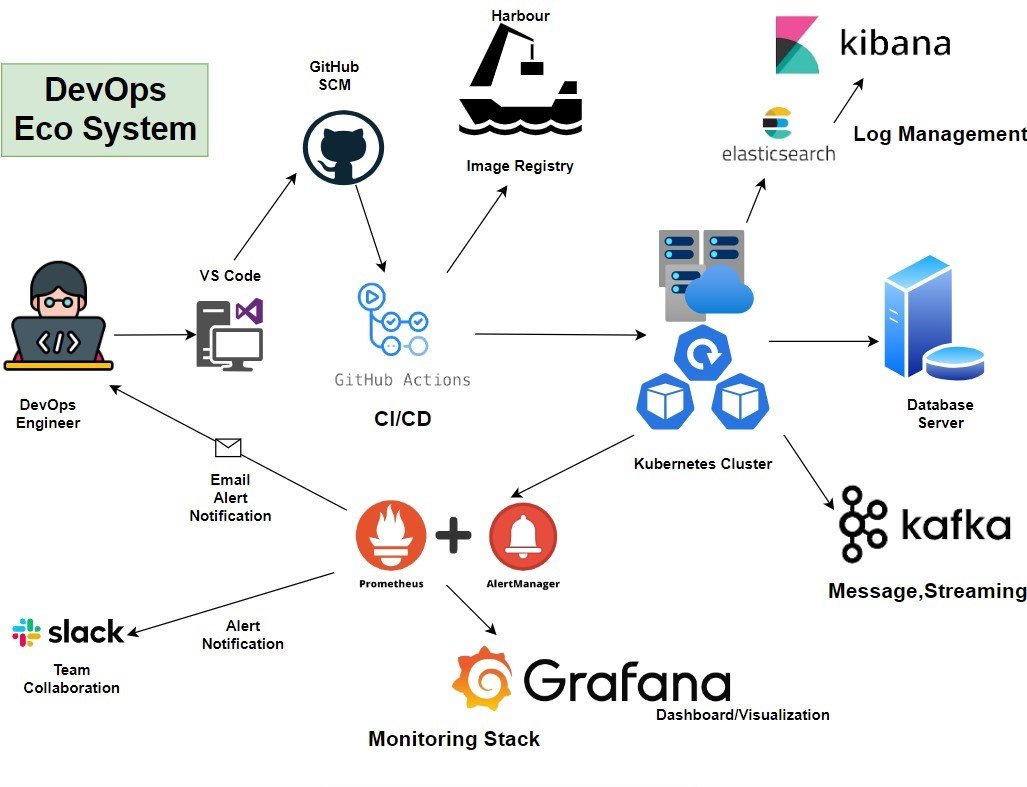
DevOps Eco System
The DevOps ecosystem refers to the interconnected set of tools, practices, and cultural elements that support the DevOps philosophy and methodology. DevOps aims to improve collaboration between development and operations teams, streamline software delivery processes, and enhance the overall efficiency and quality of software development and deployment. Tools for DevOps ecosystem:
IDE-Visual Code
VS Code is a code editor developed by Microsoft. It has gained immense popularity among developers across different platforms due to its lightweight nature, extensive customization options, and support for a wide range of programming languages and frameworks.
Source Code Management-Git Hub
GitHub is a web-based platform for version control using Git, a distributed version control system. It offers a wide range of features designed to facilitate collaboration among software developers and streamline the process of managing and sharing code.
CI/CD-GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a powerful automation tool provided by GitHub, a widely used platform for hosting and collaborating on code repositories. It allows developers to automate various tasks directly within their GitHub repositories, such as building, testing, and deploying code, as well as performing other workflow-related actions.
Here’s how GitHub Actions typically work:
Workflow Definition: Workflows in GitHub Actions are defined using YAML files. These YAML files specify the sequence of tasks, or “jobs,” that should be executed when certain events occur, such as pushing code to a repository, creating a pull request, or scheduling a periodic job.
Events Triggering Workflows: Workflows are triggered by specific events that occur within the repository. These events can include actions like pushing code changes, opening or closing pull requests, creating new releases, or even external events like a scheduled timer.
Jobs and Steps: Each workflow consists of one or more jobs, and each job comprises one or more individual steps. Jobs are executed in parallel by default, but you can also configure dependencies between them. Steps within a job define individual actions to be performed, such as checking out code from the repository, running tests, building artifacts, or deploying applications.
Actions Marketplace: GitHub Actions provides a vast ecosystem of pre-built actions that can be used within workflows. These actions encapsulate common tasks and can be easily integrated into your workflows. Additionally, you can create and share your own custom actions with the community.
Environment Setup: GitHub Actions provides various execution environments for running workflows, including Linux, Windows, and macOS. You can also specify custom virtual environments or containers to execute your workflows, ensuring compatibility with your project’s requirements.
Visibility and Logs: GitHub Actions provides detailed logs for each workflow run, allowing developers to troubleshoot issues and track the progress of their automation tasks. You can also view the status of workflows directly within the GitHub UI, making it easy to monitor and manage your automation processes.
Overall, GitHub Actions streamline the development workflow by automating repetitive tasks, improving productivity, and enabling continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) practices within GitHub repositories.
Image Registry- Harbor
Harbor Registry is a container image registry solution provided by VMware,its significance in the context of containerized applications and Docker environments
Containerized Deployment- Kubernetes Cluster
Kubernetes is an container orchestration platform ,automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, allowing organizations to run resilient, scalable, and portable workloads across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Log Analysis- Elastic Search/Kibana
Elasticsearch and Kibana are two components of the Elastic Stack, commonly referred to as the ELK Stack. They are widely used for searching, analyzing, and visualizing large volumes of data.
Message Streaming- Kafka
Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform from Apache used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. It was originally developed by LinkedIn and later open-sourced as part of the Apache Software Foundation. Kafka is designed to handle high-throughput, fault-tolerant, and scalable data streaming scenarios.
Monitoring & Alert Management
Prometheus, Alertmanager, and Grafana are three popular open-source tools often used together for monitoring and observability in cloud-native environments. Let’s delve into each of them:
Prometheus:
Time-Series Database: Prometheus is a monitoring and alerting toolkit originally developed by SoundCloud. At its core, Prometheus serves as a time-series database designed to store and query metrics data.
Alertmanager
Alert Management and Routing: Alertmanager is a component that handles alerting and notifications in Prometheus-based monitoring setups. It receives alerts from Prometheus and performs various tasks such as deduplication, grouping, routing, and silencing.
Grafana
Visualization and Dashboarding: Grafana is a popular open-source visualization and dashboarding tool used for creating and sharing interactive dashboards. It supports a wide range of data sources, including Prometheus, and provides a rich set of visualization options such as graphs, charts, and tables.
Team Collaboration-Slack
Slack is a widely used cloud-based collaboration platform that facilitates communication and teamwork within organizations. It provides a variety of features and tools to help teams communicate effectively, share information, and collaborate on projects in real-time
Cultural elements such as shared goals, cross-functional collaboration, continuous learning, and feedback-driven improvement are fundamental to the DevOps mindset. DevOps practices such as Agile methodologies, DevSecOps, site reliability engineering (SRE), and blameless postmortems promote a culture of accountability, innovation, and continuous improvement.
Overall, the DevOps ecosystem encompasses a wide range of tools, practices, and cultural aspects that enable organizations to adopt and implement DevOps principles effectively, driving agility, efficiency, and innovation in software development and delivery.